
Vinho Verde
The Vinho Verde region
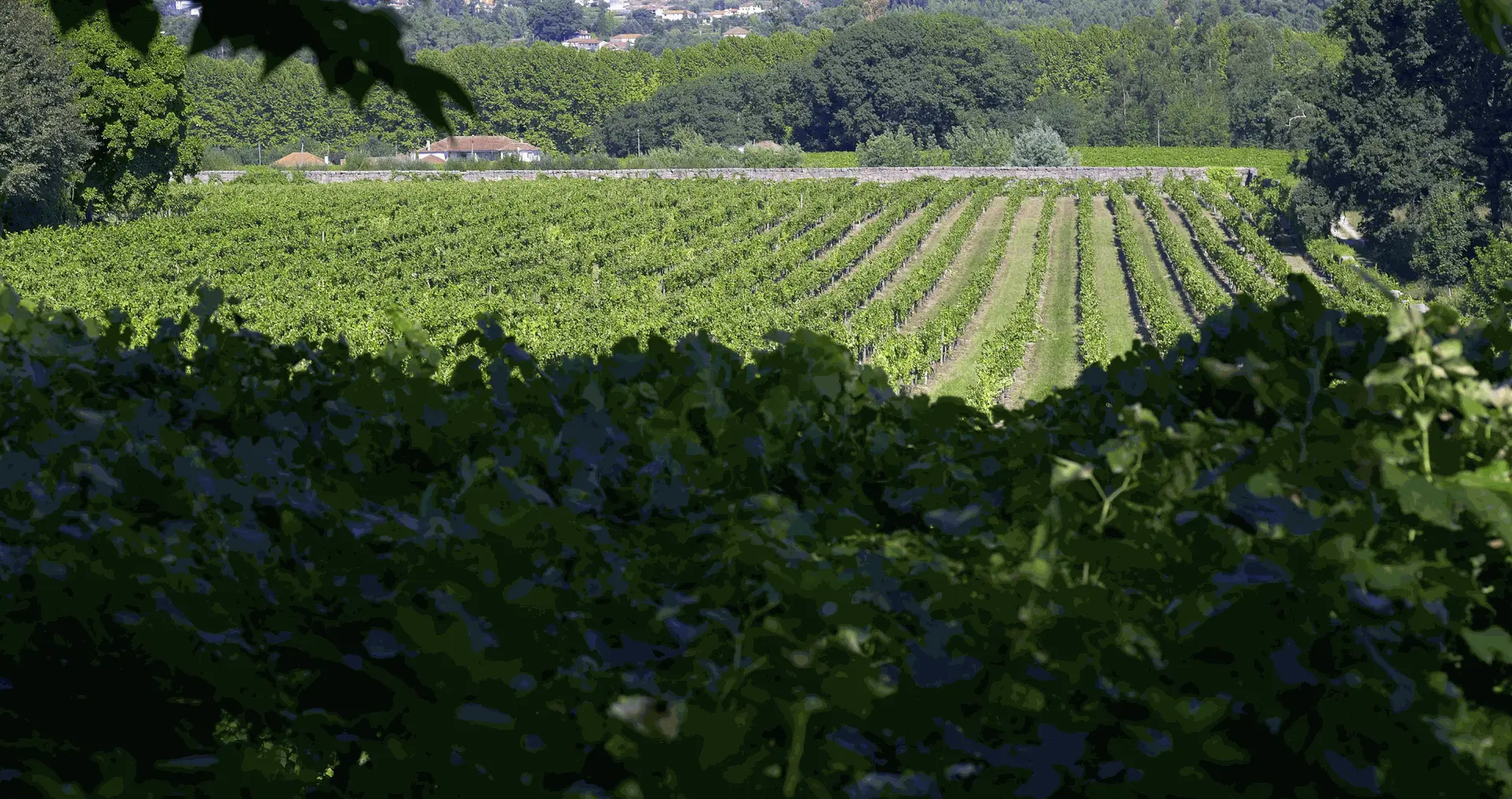
The Vinho Verde is one of the most original regions of Portugal, characterised by a strong Atlantic influence, a lush and humid landscape, cool temperatures, and abundant rainfall. It is the largest appellation in the country, covering approximately 24,000 hectares in the north-west of Portugal, with thousands of often tiny plots.
The region extends from the Spanish border, along the Minho River, to Porto and south to the Vouga River. The vineyards are concentrated in the valleys of the main rivers, on fertile and acidic granite soils.
The Vinho Verde is divided into nine sub-regions: Monção e Melgaço, Lima, Basto, Cávado, Ave, Amarante, Baião, Sousa and Paiva. Monção e Melgaço, sheltered from the direct influence of the Atlantic, produces fuller-bodied and more alcoholic wines.
The cultivation techniques are unique, ranging from the "enforcado" vine (intertwined in trees) to pergola systems ("latada") and simple cordon.
The main white grape varieties are Alvarinho, Arinto (Pedernã), Avesso, Azal, Loureiro, and Trajadura. For the reds, there are Borraçal, Brancelho, Espadeiro, and Vinhão.
White wines are distinguished by their freshness, clarity, and aromas. Since 1999, the region has also been producing sparkling wines, promising in terms of quality.
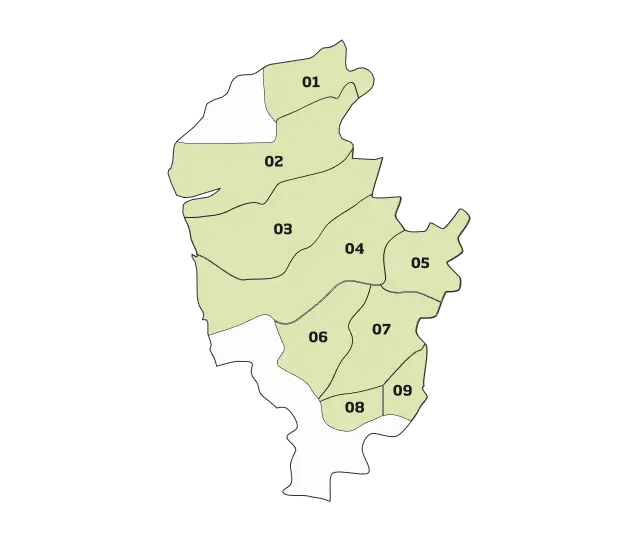
Sub-regions:
01: Monção
02: Lima
03: Cávado
04: Ave
05: Basto
06: Sousa
07: Amarante
08: Paiva
09: Baião